Imperial Home Services offers radon testing for residential and commercial properties.
Imperial Home Services provides DEP certified radon measurement specialists to perform radon testing in your home or business.
Imperial Home Services provides accurate, dependable results!
Radon Testing Pricing:
| 48 Hour Short term test (No home inspection) | $150 |
| Follow-up test (If radon is found and remediation system installed) | $100 |
| If part of a paid home inspection | $75 |
What is Radon?
Radon is a cancer-causing radioactive gas. You cannot see, smell or taste radon, but it may be a problem in your home. The Surgeon General has warned that radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States today. If you smoke and your home has high radon levels, you’re at high risk for developing lung cancer. Some scientific studies of radon exposure indicate that children may be more sensitive to radon. This may be due to their higher respiration rate and their rapidly dividing cells, which may be more vulnerable to radiation damage.
Why should I test my home for Radon?
Testing is the only way to know your home’s radon levels. There are no immediate symptoms that will alert you to the presence of radon. It typically takes years of exposure before any problems surface.
The US EPA, Surgeon General, American Lung Association, American Medical Association, and National Safety Council recommend testing your home for radon because testing is the only way to know your home’s radon levels. There are no immediate symptoms that will alert you to the presence of radon. It typically takes years of exposure before any problems surface.
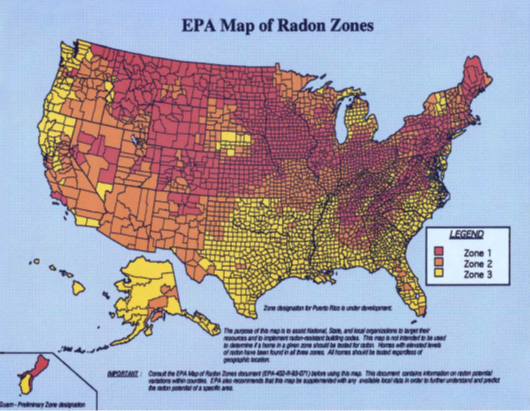
Radon is a national environmental health problem. Elevated radon levels have been discovered in every state. The US EPA estimates that as many as 8 million homes throughout the country have elevated levels of radon. Current state surveys show that 1 home in 5 has elevated radon levels.
I’m buying a house. Should I have it tested for radon?
The EPA recommends that all houses, regardless of what radon zone the house is located in, be tested for radon during point of sale. The most common procedure for radon testing during real estate transactions is for the potential buyer to request the radon test as part of the overall home inspection.
If the radon test is 4 pCi/L (Picocuries per liter of water) or greater, the EPA recommends the potential buyer negotiate with the seller to have a radon mitigation system installed with the stated goal of bringing the radon level in the home below 4 pCi/L.
I’m selling a house. Should I have it tested for radon?
The homeowner of a house can have their home tested for radon prior to listing the home for sale. If the homeowner does have a radon test performed in their home, most if not all states will require that the test result be disclosed on the whole house disclosure form you will fill out with your realtor. If the initial test comes back less than 4 pCi/L, potential buyers may still request an additional radon test as part of their home inspection. If an initial radon test by the homeowner is 4 pCi/L or greater, the issue will need to be addressed in the real estate transaction.
A buyer may want to have a confirmatory test conducted. With an average radon level of 4 pCi/L or greater, it is recommended that a radon mitigation system be installed prior to placing the house on the market, to bring the radon level to less than 4 pCi/L.
Why is radon the public health risk that it is?
Read EPA’s Citizen’s Guide to Radon: The Guide to Protecting Yourself and Your Family From Radon
EPA estimates that about 20,000 lung cancer deaths each year in the U.S. are radon-related. Exposure to radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. Radon is an odorless, tasteless and invisible gas produced by the decay of naturally occurring uranium in soil and water. Radon is a form of ionizing radiation and a proven carcinogen. Lung cancer is the only known effect on human health from exposure to radon in air. Thus far, there is no evidence that children are at greater risk of lung cancer than are adults.
Radon in air is ubiquitous. Radon is found in outdoor air and in the indoor air of buildings of all kinds. EPA recommends homes be fixed if the radon level is 4 pCi/L (picocuries per liter) or more. Because there is no known safe level of exposure to radon, EPA also recommends that Americans consider fixing their home for radon levels between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L. The average radon concentration in the indoor air of America’s homes is about 1.3 pCi/L. It is upon this level that EPA based its estimate of 20,000 radon-related lung cancers a year upon. It is for this simple reason that EPA recommends that Americans consider fixing their homes when the radon level is between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L. The average concentration of radon in outdoor air is .4 pCi/L or 1/10th of EPA’s 4 pCi/L action level.
The radon health risk is underscored by the fact that in 1988 Congress added Title III on Indoor Radon Abatement to the Toxic Substances Control Act. It codified and funded EPA’s then fledgling radon program. Also that year, the Office of the U.S. Surgeon General issued a warning about radon urging Americans to test their homes and to reduce the radon level when necessary (U.S. Surgeon General).
Unfortunately, many Americans presume that because the action level is 4 pCi/L, a radon level of less than 4 pCi/L is “safe”. This perception is altogether too common in the residential real estate market. In managing any risk, we should be concerned with the greatest risk. For most Americans, their greatest exposure to radon is in their homes; especially in rooms that are below grade (e.g., basements), rooms that are in contact with the ground and those rooms immediately above them.
It’s never too late to reduce your risk of lung cancer. Don’t wait to test and fix a radon problem.